The Cell : Steps of Protein Production
Step 1
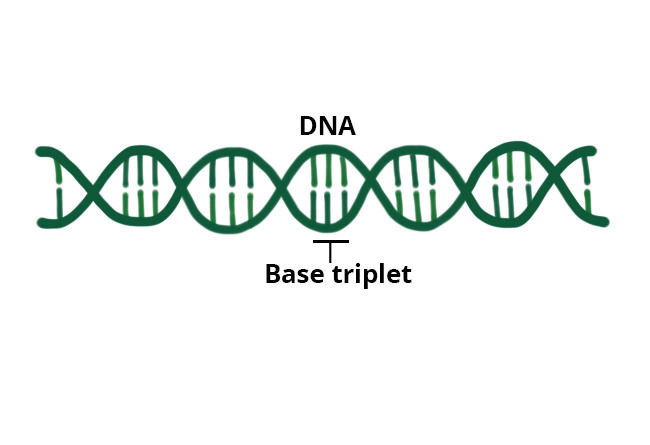
All of the information required to synthesise proteins is stored in DNA, a double-stranded helix molecule located within the nucleus. The segment of DNA that stores the specific information for a single protein is called a gene. DNA stores genetic information as sets of three nucleotides; each set is called a base triplet.
Step 2
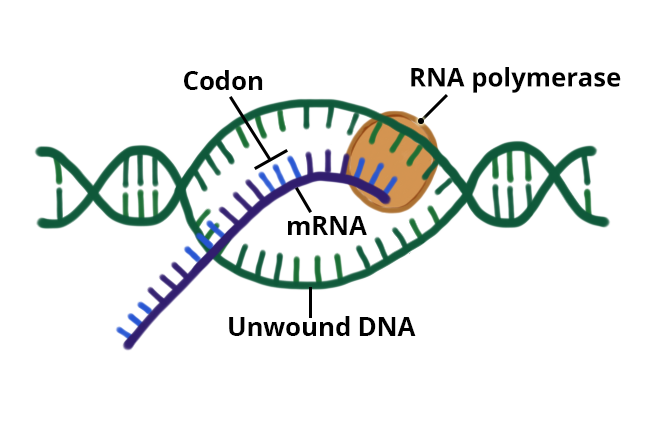
Genetic instructions for making a protein are copied from DNA onto a single-stranded messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This process is called transcription. During transcription, a segment of the DNA molecule is opened, and an enzyme called RNA polymerase uses the genetic information represented by the sequence of base triplets in DNA as a template to create a complementary sequence of codons that form the mRNA strand.
Step 3
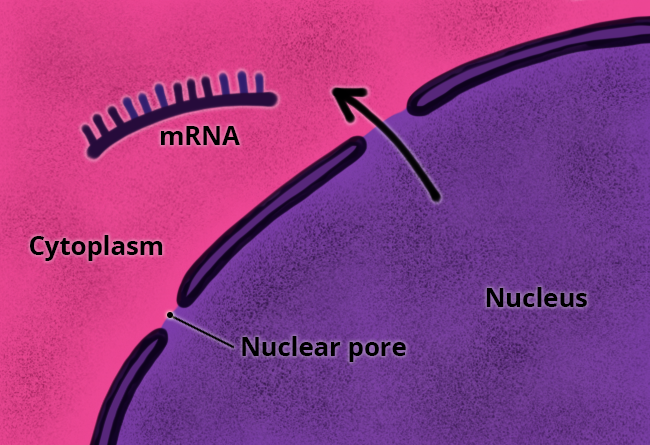
mRNA leave the nucleus via nuclear pores and travel to a ribosome in the cytoplasm (either a free ribosome or a ribosome on rough endoplasmic reticulum). Information in the mRNA is then used to construct a protein from building block elements called amino acids. This process is called translation.
Step 4
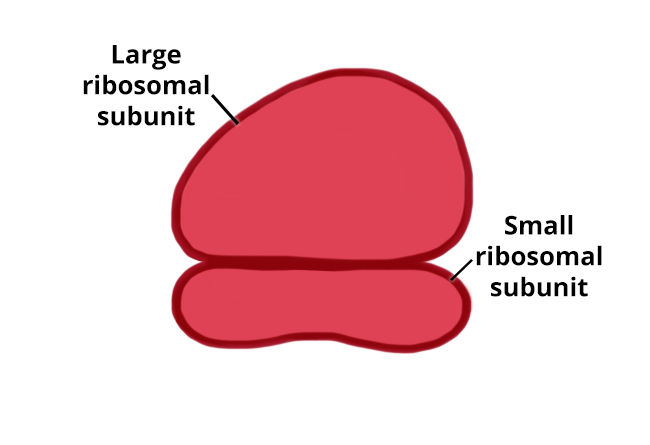
Ribosomes are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins. Each ribosome consists of a large and a small subunit that are made separately in the nucleolus of the nucleus, but then assemble together in the cytoplasm.
Step 5
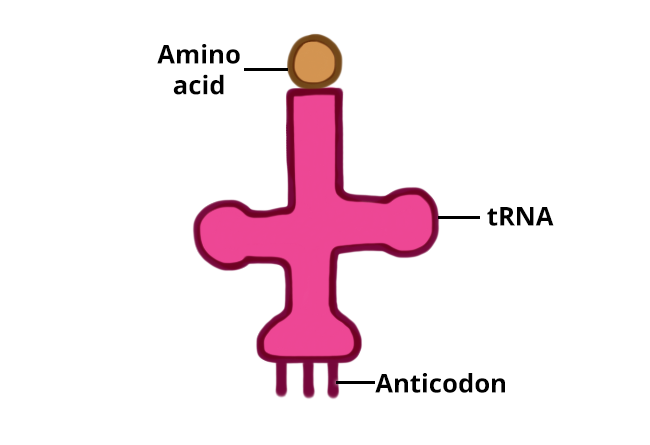
During translation, amino acids are delivered to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, and the opposite end consists of a triplet of nucleotides called an anticodon, which binds to the corresponding codon on the mRNA. There are 20 different amino acids, so the function of tRNA is to deliver the correct amino acid to the ribosome based on the instructions (codons) provided in the mRNA molecule.
Step 6
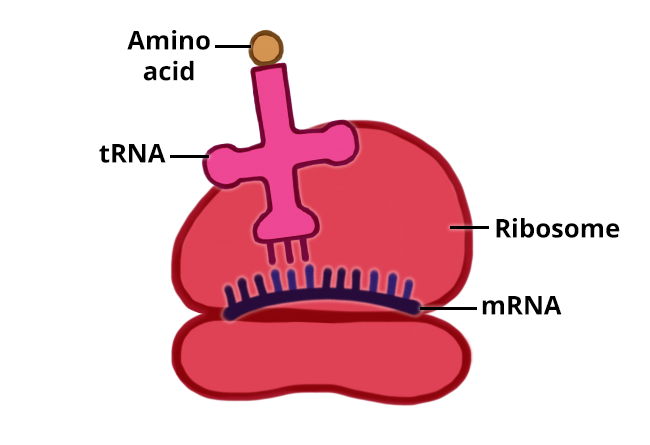
The mRNA molecule binds to the small ribosomal subunit. tRNA molecules carrying amino acids travel to the ribosome and bind to the mRNA molecule (anticodon-codon binding). The large ribosomal subunit joins the delivered amino acids together to form a protein.
Step 7
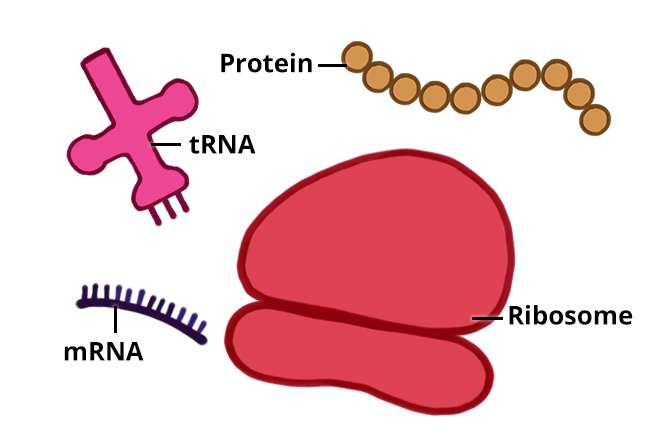
After translation is complete,
- the mRNA molecule is released from the ribosome
- ribosomal subunits disassociate, and
- synthesised protein makes its way to the Golgi apparatus for post-translational modification.