Muscular Tissue
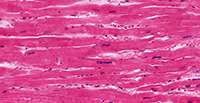
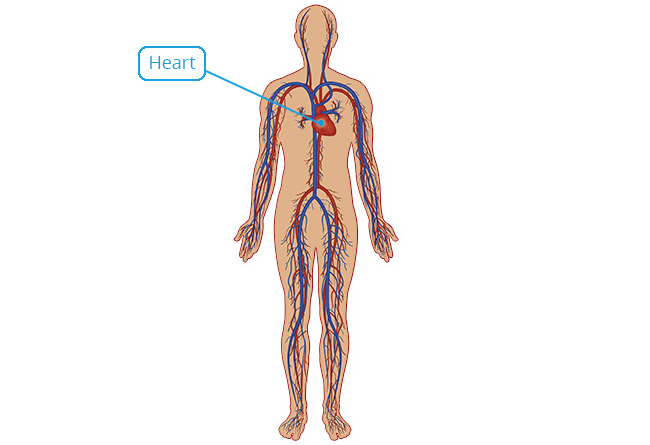
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
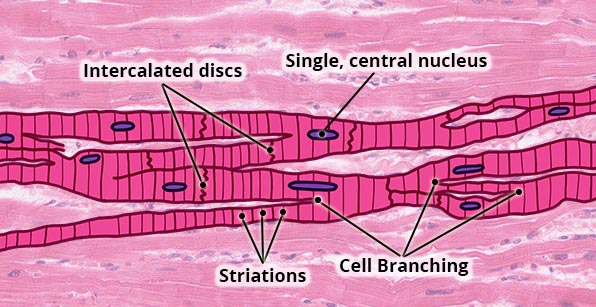
Structure
Short, branched cells; appear striated; single centrally located nucleus; adjacent cells are connected via intercalated discs which contain gap junctions and desmosomes.
Location
Heart.
Function
Pump heart, which propels blood around the body.
Nervous control
Under involuntary (subconscious) control.
Capacity for Regeneration
None; any repair is done via scar (dense, irregular) tissue.
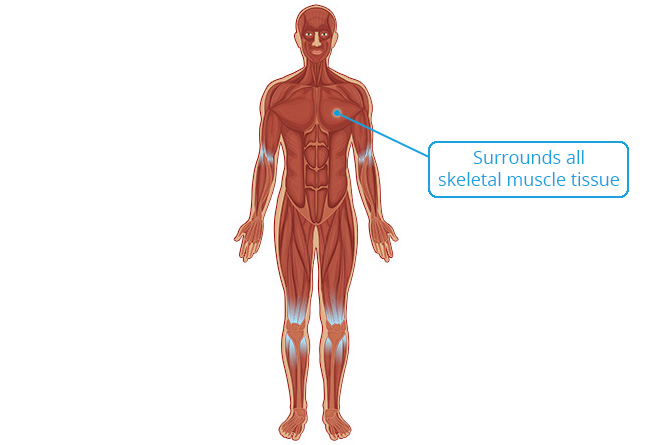
Connective Tissue Coverings of Skeletal Muscle
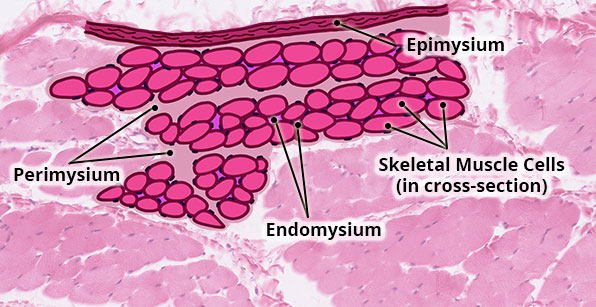
Location
Skeletal muscle cells are surrounded and protected by multiple layers of connective tissue.
Structure
Function
Connective tissue has three important functions in muscle.
- It protects muscle.
- It holds muscle cells with similar functions together so they contract in unison.
- It brings blood vessels and nerves into and out of muscle tissue.
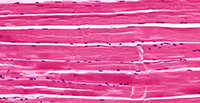
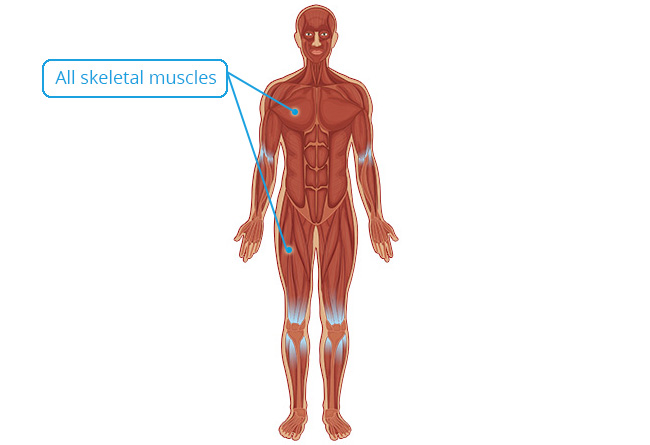
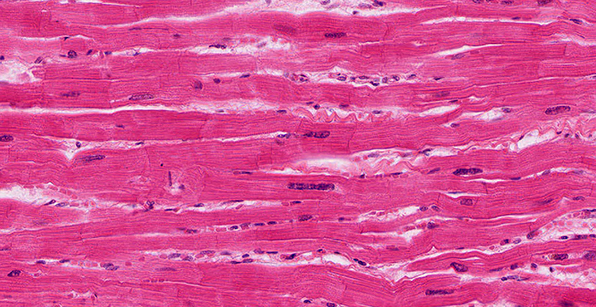
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
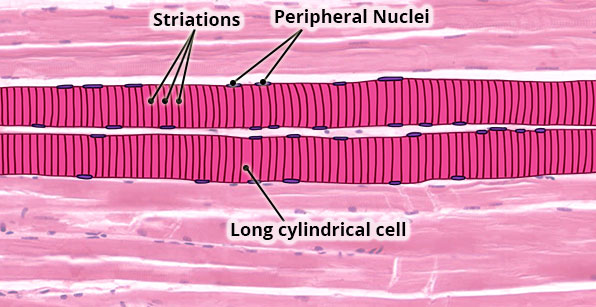
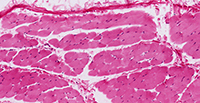
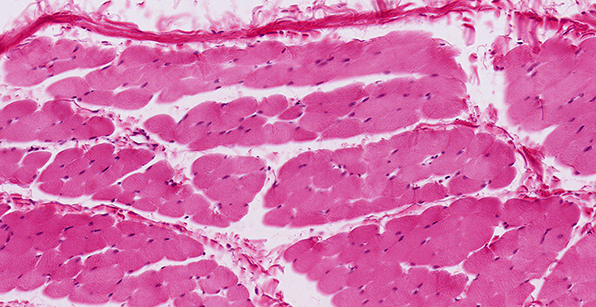
Structure
Large, long, cylindrical cells; appear striated (dark/light bands); multinucleated with nuclei located at edge of cell; no junctions between cells.
Location
Mostly attached to bones via tendons.
Function
Move the body; maintain posture; generate heat (e.g. shivering).
Nervous control
Under voluntary (conscious) control.
Capacity for Regeneration
Limited; any regeneration occurs via differentiation of satellite cells into new skeletal muscle cells.
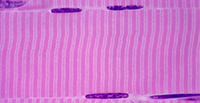
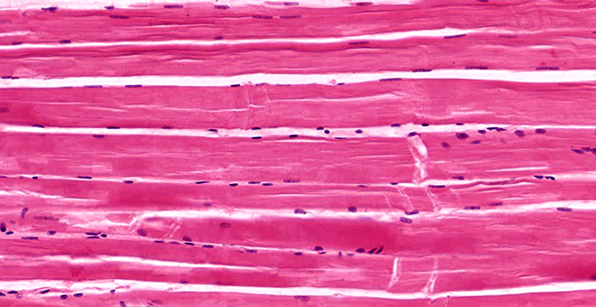
Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Magnified)
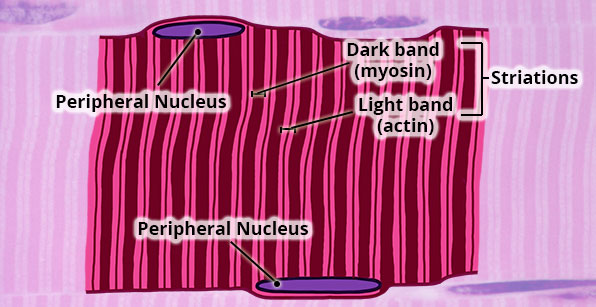
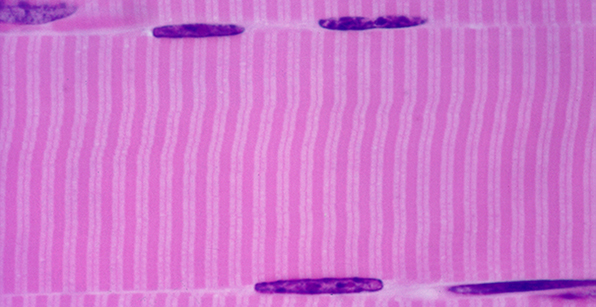
Structure
Large, long, cylindrical cells; appear striated (dark/light bands); multinucleated with nuclei located at edge of cell; no junctions between cells.
Location
Mostly attached to bones via tendons.
Function
Move the body; maintain posture; generate heat (e.g. shivering).
Nervous control
Under voluntary (conscious) control.
Capacity for Regeneration
Limited; any regeneration occurs via differentiation of satellite cells into new skeletal muscle cells.
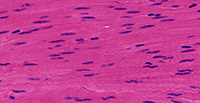
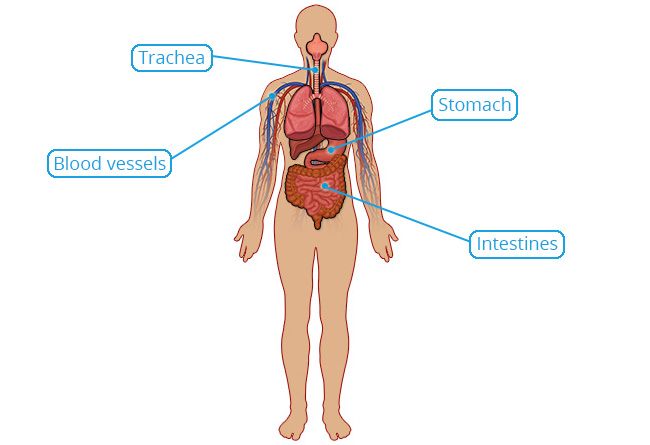
Smooth Muscle Tissue
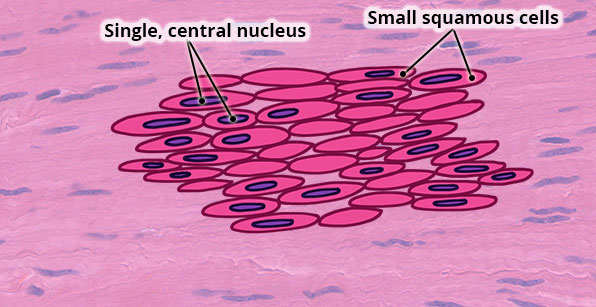
Structure
Small, squamous-shaped cell; non-striated; single centrally located nucleus; adjacent cells can be connected via gap junctions.
Location
In the wall of hollow organs (e.g. stomach, intestines) and tubes (e.g. blood vessels, trachea).
Function
Movement of food (gastrointestinal tract), blood (blood vessel), air (bronchioles) and urine (ureter, bladder and urethra).
Nervous control
Under involuntary (subconscious) control.
Capacity for Regeneration
Considerable as cells can divide.