Epithelial Tissue
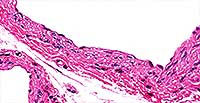
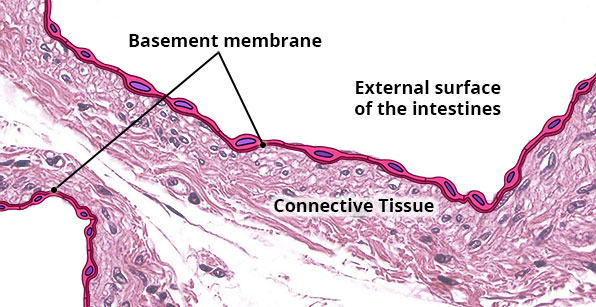
Simple Squamous
Structure
Single layer of flat cells; a bulge occurs in each cell where the nucleus is located; it is often difficult to see the cytoplasm because the cells are so thin.
Location
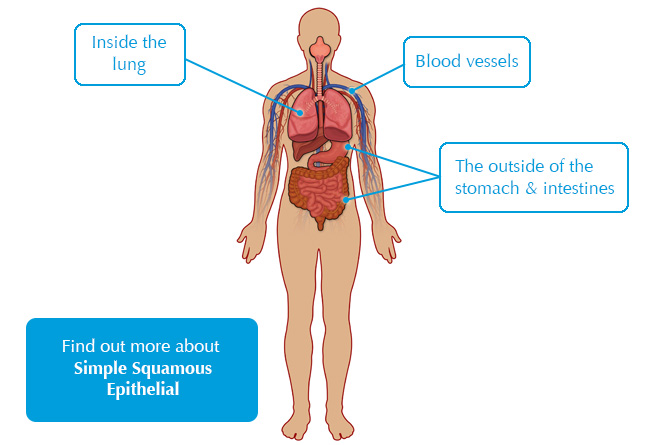
Air sacs (alveoli) of lungs; inner lining of blood vessels and heart (endothelium) and lymphatic vessels; external (serous) membranes of stomach and intestines; some tubules of kidney.
Function
Usually rapid diffusion or transport of material (lungs, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels); sometimes secretion of lubricating serous fluid (serous membranes).
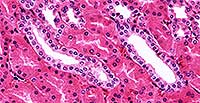
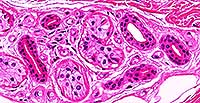
Simple Cuboidal
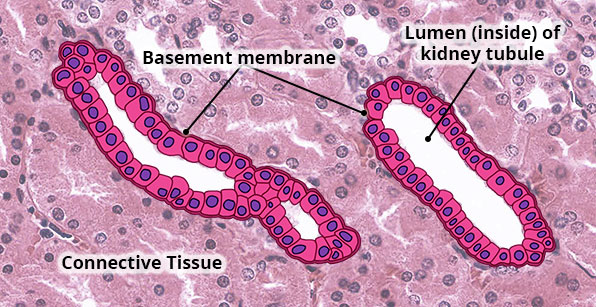
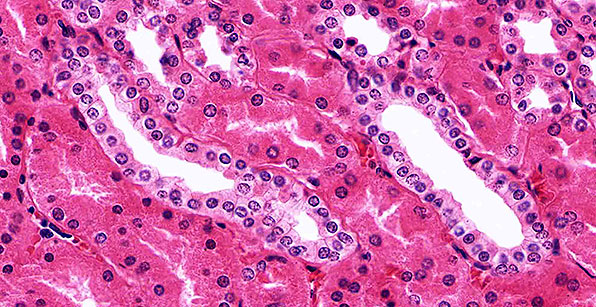
Structure
Single layer of cube or round-shaped cells.
Location
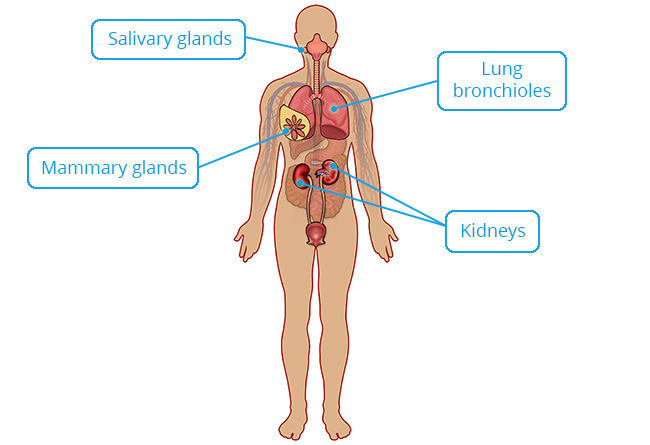
Kidney tubules; ducts of many glands including mammary and salivary; surface of ovaries; ciliated in terminal bronchioles of the lungs.
Function
Secretion and absorption.
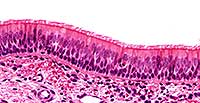
Simple Columnar
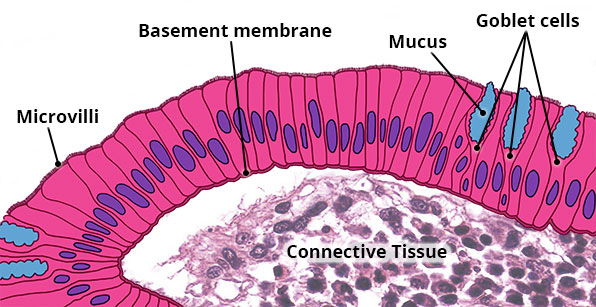
Structure
Single layer of tall, narrow column-shaped cells; oval nucleus usually near base of cell; some cells have cilia (lungs, uterine tubes) or microvilli (intestines); may possess Goblet cells which secrete mucus.
Location
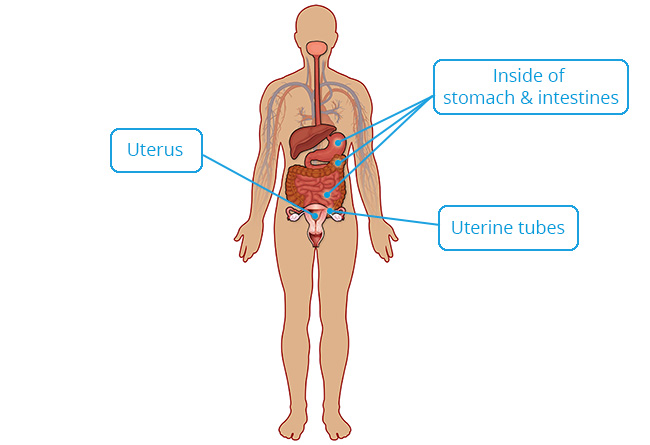
Stomach, intestines and gallbladder; uterus and uterine tubes; bronchioles of lungs; some kidney tubules.
Function
Absorption (stomach, intestines and kidney); secretion (stomach, intestines, lungs, uterus and kidney); mucus from Goblet cells helps prevent destruction of stomach lining from acidic gastric juice.
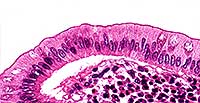
Pseudo-stratified Columnar
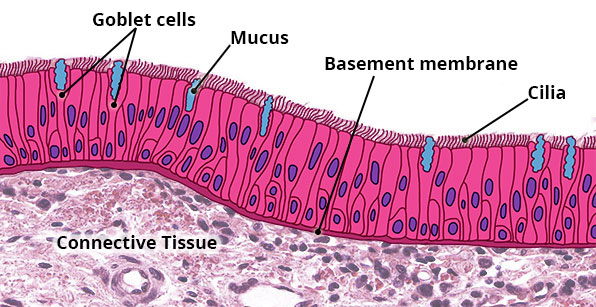
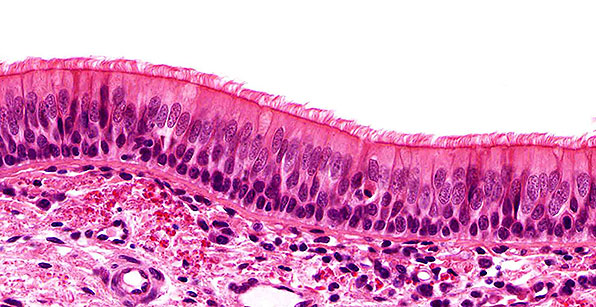
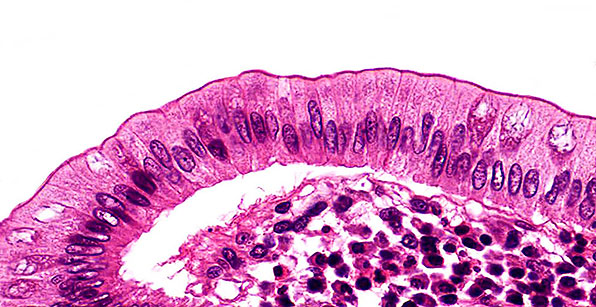
Structure
Single layer of cells of varying heights; looks multi-layered (stratified) because nuclei are located at different levels; all cells are anchored to the basement membrane but only some cells reach the free surface; almost always ciliated and associated with Goblet cells which secrete and secrete mucus.
Location
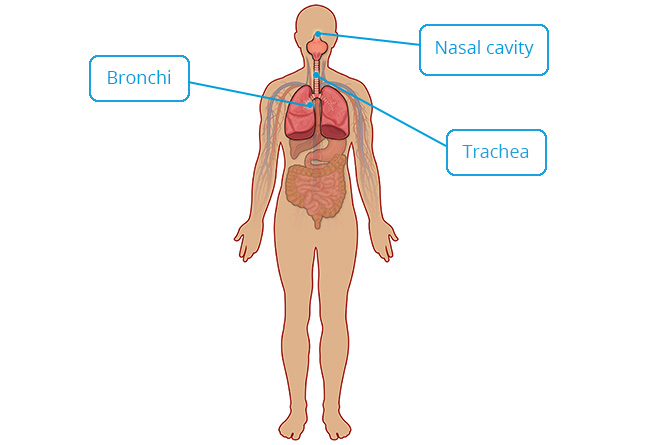
Respiratory tract from nasal cavity to bronchi.
Function
Mucus traps dust in air and foreign material; cilia sweep mucus and trapped material towards the throat where it is coughed or swallowed or spat out.
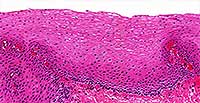
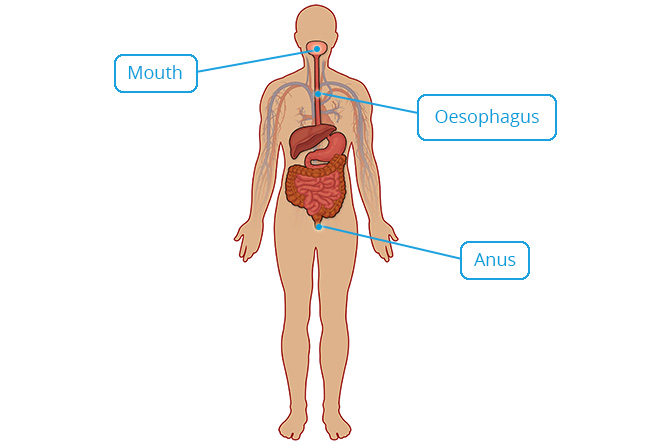
Stratified Squamous
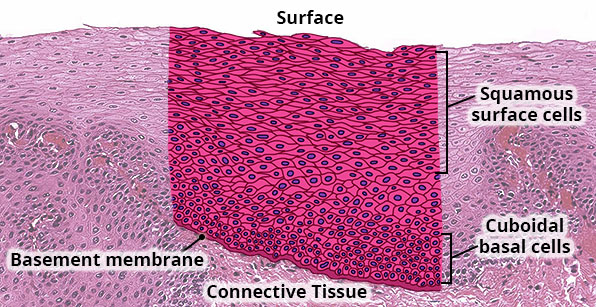
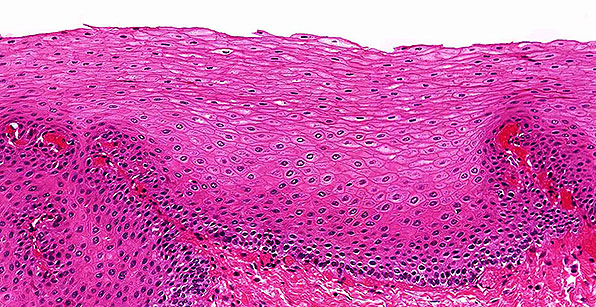
Structure
Multiple layers of cells; cells are cuboidal in basal layers and progressively flatten towards the surface.
Location
Mouth, throat, larynx and oesophagus; anus; vagina; cornea.
Function
Protection against abrasion and pathogenic invasion.
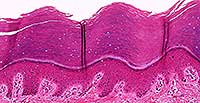
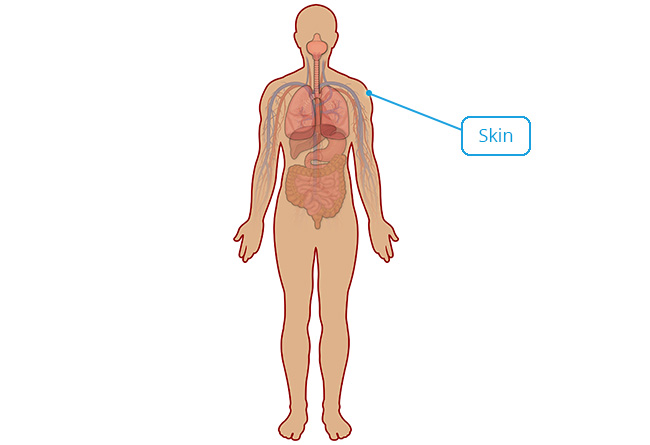
Stratified Squamous Keratinised
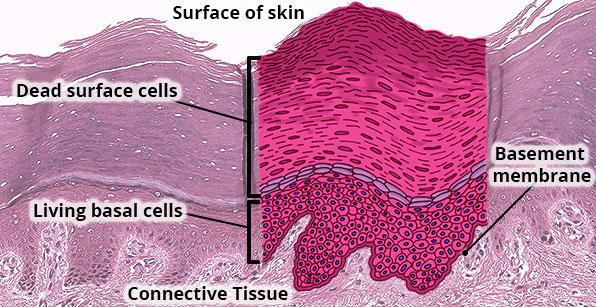
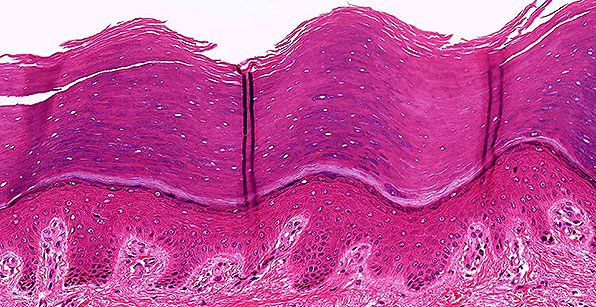
Structure
Multiple layers of cells; cells are cuboidal in basal layers and progressively flatten towards the surface; surface is covered with layers of compact dead cells without nuclei and filled with a tough protein called keratin.
Location
Skin.
Function
Protection against abrasion and pathogenic invasion; retards water loss through skin.
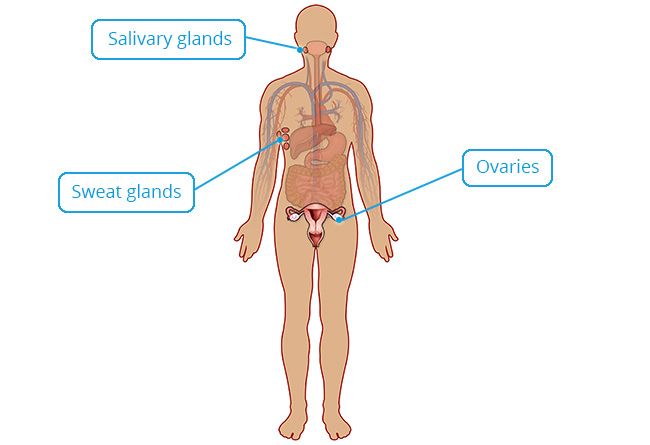
Stratified Cuboidal
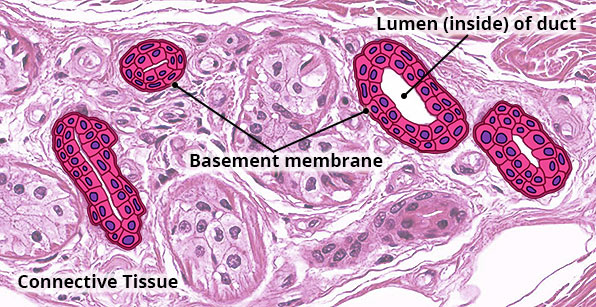
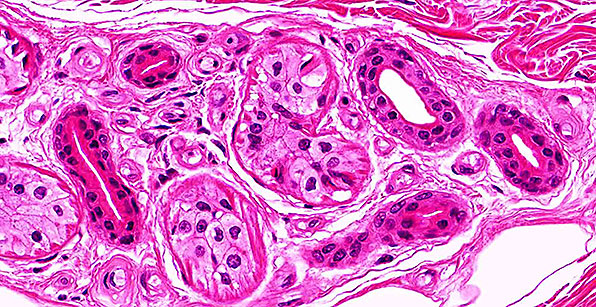
Structure
Two or more layers of cube-shaped cells; rare type of epithelium.
Location
Ducts of sweat and salivary glands; ovarian follicles; sperm-producing ducts (seminiferous tubules).
Function
Secretion (glands, ovarian hormones, sperm); protection.
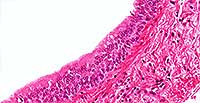
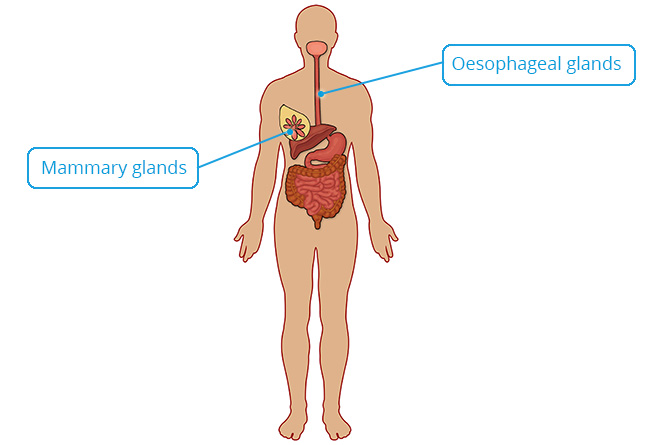
Stratified Columnar
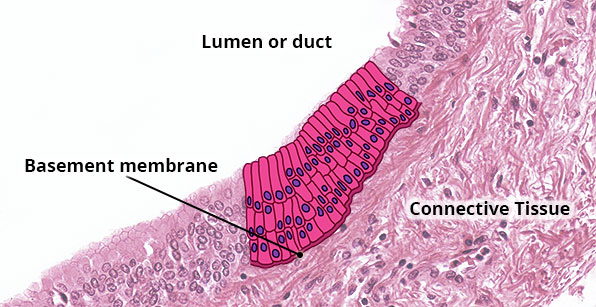
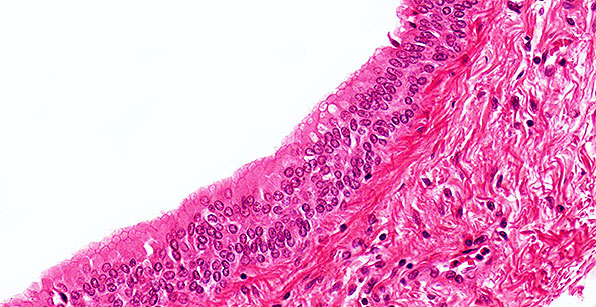
Structure
Multiple layers of column-shaped cells usually resting on cuboidal cells; rare type of epithelium.
Location
Ducts of mammary and oesophageal glands; part of male urethra.
Function
Protection; limited secretion.
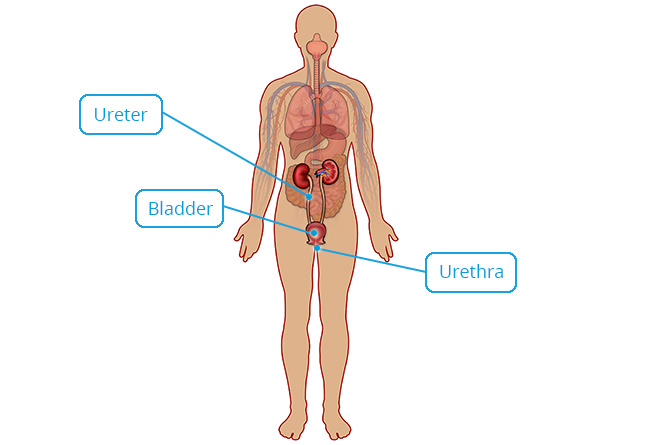
Transitional
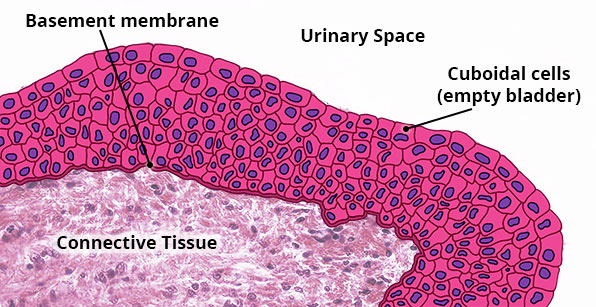
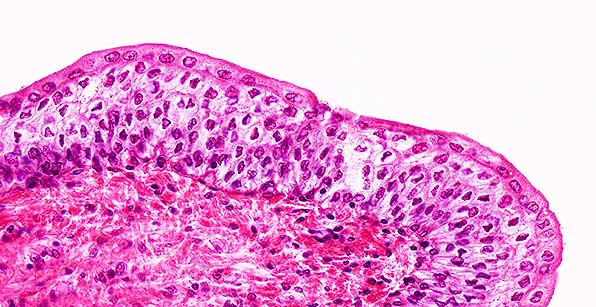
Structure
Multiple layers of cells that can change shape; cells are cuboidal when bladder is empty, but become squamous as bladder distends (stretches) when it fills with urine.
Location
Urinary bladder; ureters; superior urethra.
Function
Allows urinary organs to stretch when filled with urine; protection against caustic urine.